目录
GIT
一、为什么要使用代码版本控制系统
- 历史版本的说明、存储与备份
- 便于团队协同合作
- 便于查看代码差异、变动历史
二、GIT 与 SVN 的区别
- GIT 为分布式的,GIT 工程每个副本都是一个备份;而 SVN 是非分布式的,依赖一个中心服务器;
- SVN 只有一个中心服务器,GIT 可以有0个或多个远端备份;svn是提交,git是同步;
- SVN 得连接中心服务器才能查看历史log; 而git不用;
- GIT 以元数据方式存储(于.git隐藏目录);SVN 以文件方式存储;
- SVN 的分支是一个完整文件目录;而 git 只保持一份本地文件目录,切换分支直接改变该目录文件;
- GIT 没有全局唯一版本号;SVN 有;
- git 可以打 tag 来弥补;但是 tag 只与 commit id对应,而 commit id 不能保证代码的唯一性(因为不同分支的同一 commit id 之前的提交历史可能不一样),所以要保证 tag 唯一性,可额外人为规定只有主分支打的tag是有效的。
三、GIT 资料
Installation
- 查看官网http://git-scm.com来下载安装
- CentOS yum 默认只有1.7.1 版本, 但像github.com等网站需要高于此版本. 此时需要源码安装升级.
Tools
- 显示仓库信息onefetch, 这个不错
Usage
- Inside .git, 介绍 .git 文件夹内容
Ignore
- 白名单的写法为:
* !.gitignore # whitelist `src` directories and their children, regardless of place !src/ !src/**/ !src/**/*.h !src/**/*.cpp !/docs/ !/docs/*.md
Submodule
- 简单概括:父项目只记录子模块的commit id,任何和“子模块”常识违背的额外操作,想想这个就理解了
但不能接受 - 新增Submodule:
git submodule add <repository 位置> <欲放置的位置> # 增加一個新的 submodule git add .gitmodules <放置的位置> git commit -m "Add submodule into version control" # 提交修改 git submodule init # 初始化.git/config
- 更新已安裝的Submodule,需额外手动更新子模块:
cd your-submodule-folder # 进入子模块所在文件夹 git pull origin master # 更新子模块,这里不会更新父项目 cd ..//回父项目目录 git add your-submodule-folder git commit -m "static/platform submodule updated" # 这里实际只提交了子模块commit id
- 团队人员使用 Submodule:
git submodule init git submodule update # 或一条命令循环初始化及更新子模块 git submodule update --init --recursive
- 修改Submodule的内容:
# 直接进入子模块文件夹,进行常规git操作 cd your-submodule-folder git add something git commit -m "modify something" cd .. # 还要回父项目根目录进行更新 git add your-submodule-folder git commit -m 'Submodule updated' git push
- 移除Submodule:
# 先砍掉目录 git rm --cached <欲移除的目录> rm -rf <欲移除的目录> # 修改 .gitmodules,将相关内容移除 vim .gitmodules # 再修改 .git/config,将相关内容移除 vim .git/config # 提交修改 $ git add .gitmodules $ git commit -m "Remove a submodule" # 安全起见再做个 sync: $ git submodule sync
Git补丁
- 一般打git补丁步骤
git diff > ../sync.patch # 生成补丁 git apply ../sync.patch # 打补丁 git apply --check ../sync.patch # 测试补丁能否成功
- git format-patch
git format-patch -1 git am
Tips
- 查看暂存区(git add 的内容)的修改:
git diff –staged或git diff –cached - 查看每次修改的文件统计(不显示具体代码修改):
git whatchanged --stat # 或者 git log --name-status
- 设置git走本地代理
#只对github.com git config --global http.https://github.com.proxy socks5://127.0.0.1:1080 #取消代理 git config --global --unset http.https://github.com.proxy)
- 增加远程仓库
git remote add [repo_name] git@remote_repo
- 选择远程仓库push
git push [repo_name] [branch]
- 删除远程仓库分支:
git push origin --delete branchname
- 删除本地的远程分支追踪(比如在远程分支删除后本地
git branch -a还有遗留remote分支)git branch -r -d origin/your_branch_name
- 同步本地的远程分支追踪
git remote prune origin
- 打tag最好用-a -m ,多一个obj,方便管理
git tag -a tagname -m "message" [commit]
- 删除远程仓库tag
git push origin :refs/tags/目的标签名
解释:
# 事实上Git 的推送和删除远程标签命令是相同的,删除操作实际上就是推送空的源标签refs: git push origin 标签名 # 相当于 git push origin refs/tags/源标签名:refs/tags/目的标签名 # git push 文档中有解释: # tag <<tag>> means the same as refs/tags/<tag>:refs/tags/<tag>. # Pushing an empty <src> allows you to delete the <dst> ref from the remote repository.
- merge 分支后, 如果隐藏了分支的 commit 信息, 具体查看可以使用
git log --graph
来列出合并分支的 commit , 再一一查看.
- 撤销
git add FILE:git rm --cached FILE # 撤销文件FILE git rm -r --cached FOLDER # 撤销文件夹FOLDER
- 加个比较爽的输出
git config --global alias.lg "log --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit --date=relative"
- 合并特定的单个commit,可使用指令
git cherry-pick - 凭证存储: credential.helper,
- 如果设为store模式,将在本地明文存储用户密码,节省下次输入:
git config credential.helper store这样会明文保存密码到
~/.git-credentials
- 打印更多日志:
GIT_TRACE=2 GIT_CURL_VERBOSE=1 git clone <repo>
详见git 环境变量
- 提交空commit:
git commit --allow-empty -m "Empty"
- 修改上一次commit的message:
git commit --amend -m "new msg"
- 设置 vim 为默认编辑器:
git config --global core.editor "vim"
- 删除某文件的所有历史记录,参考:
- 查找大文件:
git rev-list –objects –all | grep “$(git verify-pack -v .git/objects/pack/*.idx | sort -k 3 -n | tail -5 | awk '{print$1}')” - 从历史记录删除:
git filter-branch -f –index-filter 'git rm –cached –ignore-unmatch “your/big.file”' HEAD –all
- 显示差异时忽略行尾空格差异:
git diff --ignore-space-at-eol
- git log 中文显示为尖括号码,修正方式:
export LESSCHARSET=utf-8
server: gitolite
Git 原理
搞懂原理后发现, git 是一个典型的, 以方便实现而设计出的工具. 所以其并没有充分考虑使用的体验. 虽然它强大, 效率高, 但对使用者来说, 命令的正交性不强这一点, 就造成了使用者需要记住大量单独的命令. 考虑找个或弄个简化版的本地版本控制系统, 或者做个git的命令包装. 这篇文章不错:https://www.highflux.io/blog/what-makes-git-hard-to-use . 这个可借鉴:https://github.com/jj-vcs/jj .
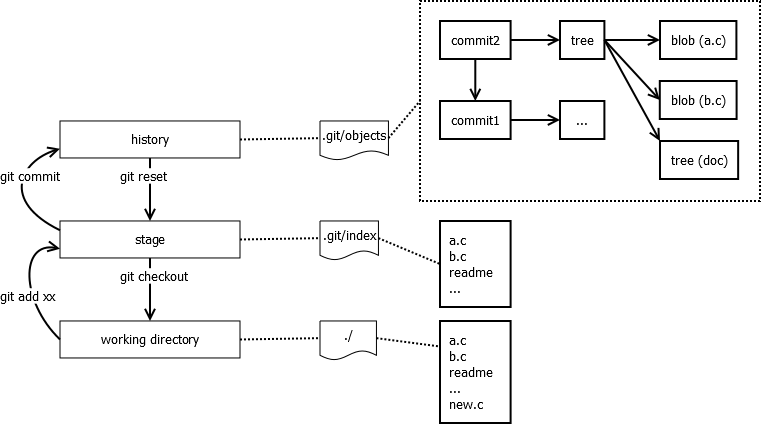
- 通过git管理的文件版本信息全部存放在项目根目录
.git下 - Git 的三个区域:
- working directory,也就是你所操作的那些文件
- history,你所提交的所有记录,文件历史内容等等。git是个分布式版本管理系统,在你本地有项目的所有历史提交记录;文件历史记录;提交日志等等。
- stage(index),暂存区域,本质上是个文件,存在于
.git/index
- Git 的存储对象,保存在
.git/objects目录,一个对象一个文件, 使用 zlib 压缩:- blob,用于表示一个文件
- tree,用于表示一个目录,索引到若干文件或子目录
- commit,用于表示一次提交(commit)
- tag , 标签对象, annotated tag, 含注释的标签
- 可使用
git cat-file子命令来查看对象. - Git 的refs 引用, 保存在
.git/refs目录下:- heads,
.git/refs/heads/存分支引用. - HEAD,
.git/refs/HEAD, 指向你当前所在分支的引用. - tags,
.git/refs/tags/, tag引用 - remotes,
.git/refs/remotes/, Git 会把你最后一次推送到远端的每个分支的值都记录在该目录下
- 子命令
git update-ref可处理大部分 refs 相关的操作